How AI Helps Combat Security Fatigue by Automating
Overwhelmed by false positives? Discover how AI-driven Digital Security Teammates can automate 70% of alert triage and restore your SOC’s sanity.
Overwhelmed by false positives? Discover how AI-driven Digital Security Teammates can automate 70% of alert triage and restore your SOC’s sanity.

Even though threat actors keep becoming more advanced, enterprise defense is currently vulnerable to one main issue: Security Fatigue. Security Fatigue is a condition characterized by mental tiredness, emotional insensitivity, and inability to act among security experts.
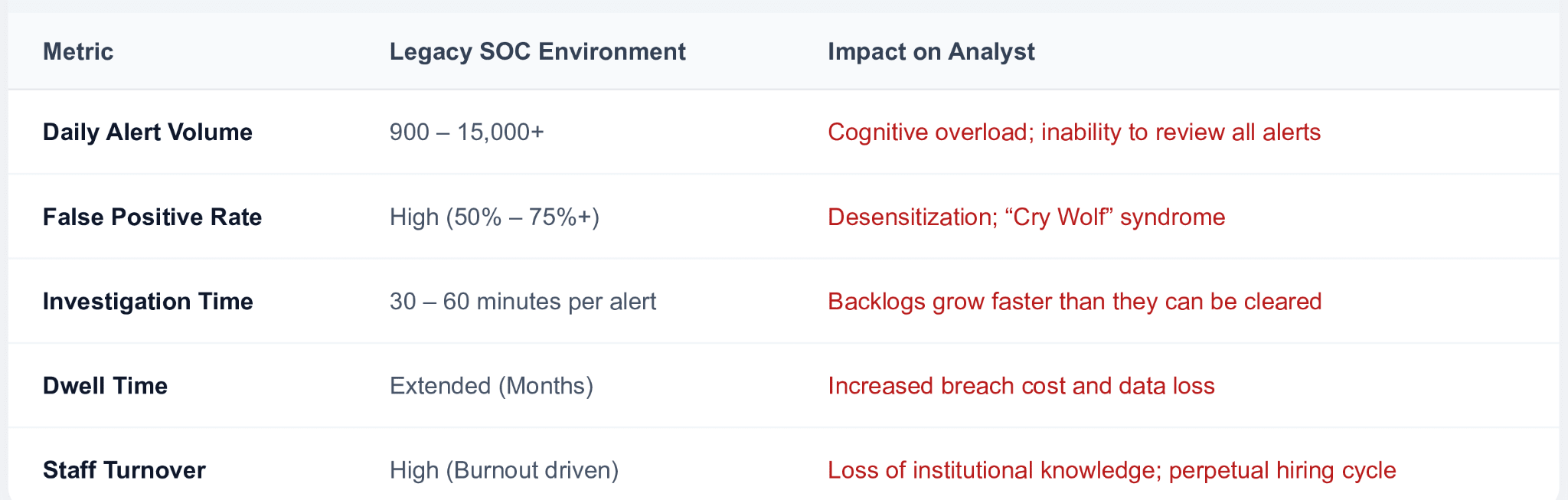
Imagine a hospital where doctors spend 80% of their shift filing paperwork while patients wait in the ER. That is the current state of cybersecurity. With the average SOC facing over 4,000 alerts every single day, analysts are drowning in noise rather than fighting threats. This isn’t a shortage of talent; it’s a failure of leverage. By shifting manual triage to AI-driven automation, we can finally stop the burnout cycle and let defenders do what they do best: defend.
Security fatigue is the cognitive exhaustion that occurs when individuals in the security field are given too many warnings to handle. This type of fatigue is very common in the contemporary SOCs; if you get alerts on the incoming seconds, you will become insensitive with time, it can’t be otherwise mathematically speaking.
These effects are very serious. According to industry studies, there are false positive rates of about 50-75% in a normal Security Operation Center (SOC) set up although some entities record up to 83% of them that still require manual deactivation.
This is an operational debt since skilled analysts spend close to 3 hrs/day trying to fix false alarm. In the end, it gets to a point where one cannot see everything since he or she must ignore some for sanity sake due to the enormous volume of information.
Automation is the only way to scale defense at the speed of today's attacks. By delegating high-volume, low-context tasks to AI, organizations can reclaim thousands of hours of productivity.
AI-powered continuous authentication analyzes behavioral biometrics—keystroke dynamics, mouse movement patterns, and interaction timing—to verify user identity without relying solely on static passwords. Rather than raising barriers for authorized users, it lowers them but, on the other hand, immediately detects irregularities that could not be seen by a fixed regulation.
Too often, skilled analysts are reduced to ticket routers, shuffling alerts between teams rather than investigating threats. However, with the introduction of AI, this has changed since it functions as a smart assistant. Such AI investigates occurrences beforehand, collecting logs from endpoints, firewalls, and identity providers to create a comprehensive dossier. With this shift, the analyst is no longer just gathering data but making decisions as well.
Attackers increasingly use polymorphic techniques and automated tooling to generate malware variants that evade signature-based detection. AI-driven defense uses machine learning to identify behavioral patterns, such as lateral movement, privilege escalation, or unusual data access, rather than relying solely on signature-based detection. This behavioral analysis enables detection of zero-day threats and novel attack techniques that lack known indicators.
This is the most immediate impact of AI. By learning what "normal" looks like for your network, AI can autonomously filter out thousands of benign anomalies—like a marketing software update or a legitimate remote login. This "noise suppression" ensures that when an analyst’s phone buzzes, it’s for a reason.
An alert that says "Malware detected on Laptop 4" is useless without context. AI instantly correlates that alert with the bigger picture: "Malware on Laptop 4, which belongs to the CFO and is currently attempting to access the payroll database." This context allows teams to react to business risks, not just technical flags.
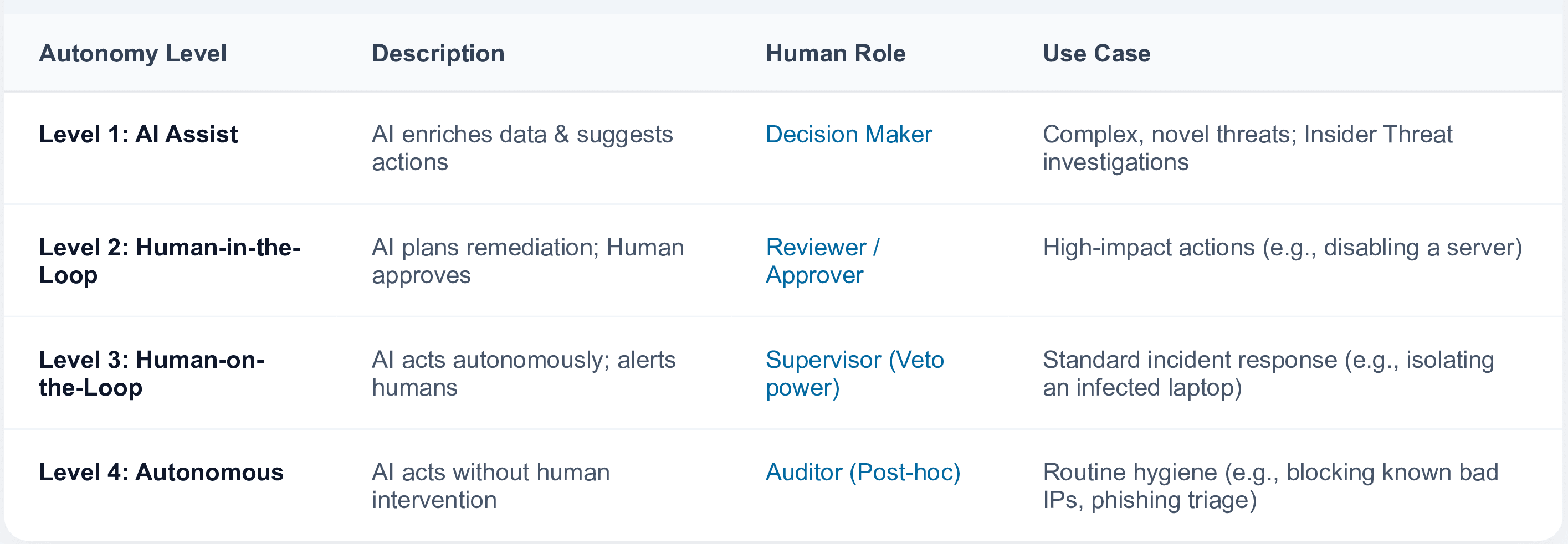
AI handles Tier 1 triage tasks, enabling teams to operate with governed autonomy—automation with human oversight for high-impact actions. AI automates safe, repetitive response actions—such as blocking known-malicious IPs or isolating compromised endpoints—reducing Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) by 45-55% while maintaining human approval for high-impact decisions. but there is no need for a human in the loop.
Data lives everywhere now, from SaaS apps to shadow IT. AI continuously scans this sprawling estate for "drift"—configurations that have become insecure over time. It acts as a 24/7 watchdog, ensuring that your data policies are being followed even when no one is watching.
Phishing Triage: AI agents automatically parse email headers, analyze URLs in sandboxed environments, and quarantine confirmed malicious emails—escalating ambiguous cases to human analysts for review. It only escalates the ambiguous cases to humans.
Impossible Travel Resolution: When a user logs in from New York and London within an hour, AI agents enrich the alert by checking VPN usage, travel itineraries, and historical patterns. For confirmed anomalies, the system can automatically suspend the account and initiate user verification via Slack—with human approval for high-privilege accounts.
Patch Prioritization: Rather than sending a list of 10,000 "Critical" vulnerabilities to IT, AI analyzes which vulnerabilities are actually exploitable in your specific environment (e.g., exposed to the internet) and prioritizes the top 5% that matter.
The most direct financial impact is the reduction in labor hours required to process alerts.
Investigation Time: AI-driven automation reduces investigation time significantly, with some organizations achieving 70% faster Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and 45-55% faster Mean Time to Respond (MTTR). An alert that previously took 30-60 minutes can be resolved in minutes.
Capacity Expansion: AI-driven automation enables SOC teams to handle significantly higher alert volumes without proportional headcount increases, with some organizations achieving 70% automation of manual triage workload. This effectively triples the capacity of the SOC without the need to hire additional headcount.
Consider an enterprise SOC: By automating 70% of alert triage and reducing MTTR by 45-55%, organizations can reclaim thousands of analyst hours annually. For example, reducing 500 hours of monthly manual work to 50 hours of review time represents significant capacity gains that can be redirected to strategic security initiatives. through personnel optimization and operational efficiency.
Organizations implementing AI-driven automation report significant time savings. For example, the KB documents one customer achieving 176 analyst hours saved per month (62% reduction in CMDB workload), translating to 2,000+ hours saved annually that can be redirected to strategic security work. just in labor capability.
The cost of security fatigue is often the cost of a missed breach.
Analyst turnover is expensive. Recruiting, hiring, and onboarding a skilled SOC analyst can cost tens of thousands of dollars, not including the "ramp-up" time where they are less effective.
At Secure.com, we believe the answer isn't just tools, but Digital Security Teammates—AI-native colleagues that augment your team's capabilities.
Security fatigue, or alert fatigue, refers to tiredness and loss of sensitivity caused by viewing many security alerts, which may result in delayed responses as well as ignoring of some dangers.
AI enables "cognitive automation." Unlike simple scripts that follow rigid rules, AI can learn patterns, understand context, and make probability-based decisions to handle complex, unstructured tasks like investigation and triage.
AI enables proactive threat prevention by analyzing behavioral patterns and identifying early-stage attack indicators—such as credential stuffing attempts, reconnaissance activity, or lateral movement—allowing teams to disrupt attacks before they achieve their objectives.
The biggest challenge is the trust gap: security teams need confidence that AI actions are appropriate and auditable. Secure.com addresses this through human-in-the-loop workflows—AI recommends actions with full reasoning traces, but requires human approval for high-impact operations like account suspension or system isolation. Every action is logged for audit and compliance.
Security fatigue represents a fundamental mismatch between SOC staffing models and exponential alert growth. It's not a talent shortage—it's a leverage gap that creates systemic risk in enterprise defense.
The evidence is clear: AI-driven automation is no longer optional for modern SOC operations—it's the only scalable path forward. With AI handling repetitive triage, security analysts evolve from alert processors to strategic defenders—focusing on threat hunting, incident response, and security architecture rather than manual data entry.
AI integration isn't just an efficiency tool—it's foundational to building a resilient, adaptive security posture capable of defending against evolving threats. In the days to come, defense will have nothing to do with humans alone or computers alone, but rather an intelligent combination of both working under mutual control and regulation.

A high-severity flaw in Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS can force firewalls into maintenance mode, creating a "digital blackout" switch for unauthenticated attackers.

Find the critical distinction between IAM (the 'Who') and RBAC (the 'What') to streamline compliance, automate user lifecycles, and secure your organization against modern threats.

Many CISOs stumble with automation by chasing tools instead of outcomes, automating low-value tasks, and leaving out human oversight.