State of AI in Cybersecurity 2025: What’s Real vs. Hype
AI promises "autonomous SOCs" that eliminate analyst burnout. But in 2025, most tools are noisy interns—not reliable teammates. Here's what actually works.
AI promises "autonomous SOCs" that eliminate analyst burnout. But in 2025, most tools are noisy interns—not reliable teammates. Here's what actually works.
AI in cybersecurity delivers real gains in alert triage and detection when deployed with human oversight. But separating vendor hype from battlefield reality requires looking at what's actually working in 2025 and beyond.
Security leaders today stand on a fault line: AI is both a guardian and a weapon. Vendors promise "autonomous SOCs" that slash detection times, while attackers use the same generative AI to scale phishing, malware, and fraud. The truth sits between marketing and mayhem, AI delivers measurable gains in alert triage and threat detection, but only with clear guardrails and human oversight. So where's the real story in 2025?
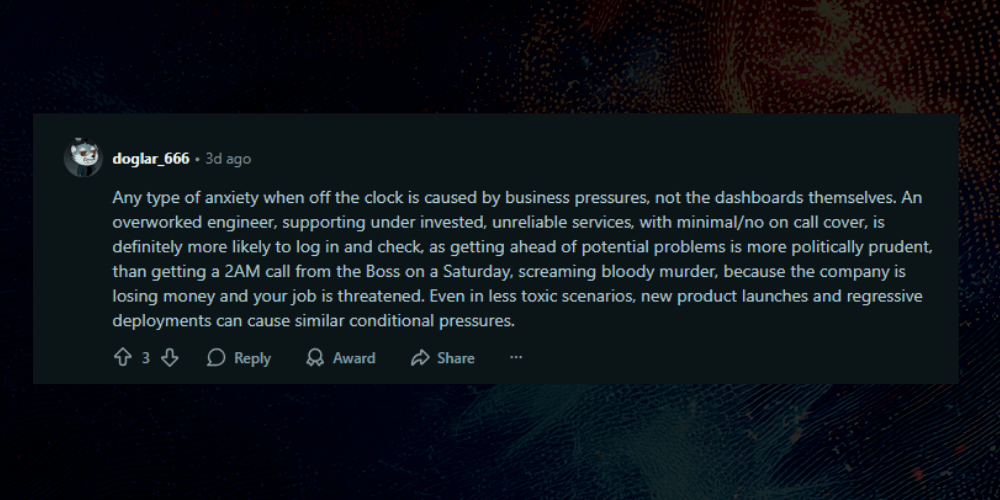
(Source: Reddit)
The biggest real-world wins are showing up in SOC triage, phishing detection, and threat intel summarization. AI helps analysts cut through noise, group alerts faster, and spot patterns that once took hours of log digging. It’s turning chaos into something closer to clarity. Most tools need babysitting, fine-tuning, and a human hand on the wheel. The real story isn’t about replacement, it’s about relief. AI cleans the room, but it doesn’t run the house.
The areas of greatest concern include:
Survey data shows that organizations are well aware of this shift:
Despite the hype-filled headlines, AI in cybersecurity is not magic. What’s emerging in 2025 is a more nuanced picture: AI is improving specific areas of defense, but its limits are becoming just as visible.
The most common “win” is in the SOC itself. According to Recorded Future’s State of AI 2025, a majority of security leaders reported measurable improvements in mean time-to-detect (MTTD) and mean time-to-respond (MTTR) after introducing AI chatbots into their workflows. These tools excel at triaging repetitive alerts, clustering similar incidents, and highlighting anomalies.
SecureWorld’s industry roundup highlights one major bank that reduced alert fatigue by 30% after layering AI models on top of its SIEM and SOAR platforms. Analysts described the AI assistant as “good at cleaning the noise so humans can focus.”
But these gains are not universal. Another Fortune 100 company saw its AI platform miss a slow, stealthy intrusion that relied on living-off-the-land techniques. The breach was eventually discovered by a human analyst. The lesson? AI improves throughput but still struggles with sophisticated adversaries.
On the phishing front, AI is proving to be an effective spam filter upgrade. MixMode reports that a significant share of phishing attempts in 2025 were flagged by AI engines as “AI-generated content” - something legacy filters couldn’t detect. This has reduced the number of low-effort phishing emails reaching employees.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025 backs this up with numbers: organizations using AI-enhanced detection saved an average of millions of dollars per breach compared to those without. AI is proving especially useful in financial fraud detection, catching anomalies in wire transfers or account takeovers that would previously slip past rule-based systems.
Still, gaps remain. Ivanti points out that in many incidents, attackers didn’t even need AI - they exploited unpatched vulnerabilities that defenders overlooked while chasing shiny AI solutions. And in the ISC2 community, practitioners share a similar caution: “AI catches the spam, but zero-days still eat us alive.”
On Reddit, SOC analysts express frustration with AI tools that generate “endless dashboards” but require constant validation. One user summarized it bluntly: “It’s not autopilot. It’s like having a noisy intern that sorts your inbox but still asks you to check everything twice.”
Taken together, the reality is this: AI works best as part of an automation framework : a structured layer that manages workflow, correlation, and validation while giving analysts room to think. The value isn’t in replacement, but relief. It works best as a filter, not a decision-maker. And in cybersecurity, that distinction matters.
The biggest misconception is that AI “thinks.” It doesn’t—it predicts. Many teams assume AI will catch novel threats by instinct when in reality it only mirrors the data it’s trained on. Another myth is that more AI means less risk. In truth, every new AI model adds another layer of attack surface.
A third misconception is that AI will replace Tier-1 analysts. Most leaders now see that as fiction. AI speeds detection, but it still needs the human sense of pattern, context, and intent to close the loop.
While defenders experiment with anomaly detection, attackers are racing ahead - and in some areas, they’re using AI more creatively than enterprises.
In 2025, phishing emails have evolved from clumsy scams to flawless corporate communications. Recorded Future reports that the percentage of phishing campaigns generated or enhanced by large language models continues to climb year over year. Unlike traditional spam, these messages mimic internal tone, borrow from leaked data, and adapt to local languages with near-perfect accuracy.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, companies using AI for detection and response saw an average reduction of millions in breach costs compared to non-AI adopters. Faster containment, fewer false positives, and automated workflows all translate to measurable savings.
But there’s another side. Licensing fees for enterprise-grade SOC chatbots have surged, and vendor lock-in creates long-term budget risks. One enterprise reported spending more on its AI security suite in 2025 than on its entire SIEM infrastructure in 2023.
Ivanti cautions that in the rush to fund AI initiatives, many companies underfund basic patch management, which remains the root cause of many breaches. AI doesn’t fix unpatched systems - and hype can create blind spots.
On Spiceworks, one analyst wrote: “AI saves time for juniors, but seniors spend twice as long validating.” That time translates directly into cost. On Quora, professionals debate whether “AI security” should be considered a new specialty or simply an inflated line item under traditional cybersecurity.
The financial equation is clear: AI saves money per breach but costs more upfront, and the balance varies by organization.
Shadow AI has become the new internal threat. Employees plug chatbots into sensitive workflows without realizing what data they’re exposing. CISOs are fighting back with guardrails, not bans. They’re building internal AI policies, tracking which models touch which data, and running quarterly audits on API use.
The smart teams don’t block AI—they manage it. Some even run “AI takes action boards” that score tools on privacy and accuracy. As one analyst joked on Reddit, “We stopped shadowing IT ten years ago. Now we’re chasing shadow AI.”
Perhaps the biggest divide isn’t technical but cultural: can analysts trust AI enough to treat it as a colleague? Analysts compare AI to “a noisy intern,” helpful but unreliable. In mature setups, a human-in-loop remains essential to maintain accountability, correct errors, and ensure actions align with policy.
What Works Today:
Intel summarization: Faster decision-making for threat intelligence teams.
SOC triage: Noise reduction and prioritization.
Phishing detection: AI filters flagging AI-written scams.
What’s Still Hype
Analyst replacement: Vendors claim AI will take over Tier-1 tasks, but case studies show human oversight remains critical
Autonomous SOCs: Gartner’s 2025 report puts autonomous SOCs at the peak of hype—widely promoted but not yet real. Most are still pilots, needing human oversight despite bold autonomy claims.
The Emerging Challenges:
Tool reliability: DEF CON’s AI Village continues to expose flaws in vendor promises, reminding the industry that AI systems are as attackable as any other software.
Regulation gaps: Agencies like CISA, NIST, and ENISA are racing to draft frameworks for AI in security, but global standards lag
The loudest myth is that AI “thinks.” It doesn’t. It predicts. Teams still confuse pattern recognition with reasoning, which leads to misplaced trust. Another myth is that AI will end cyber risk altogether. It won’t. It just moves the weak spots somewhere new.
The last misconception is that AI will replace human analysts. In truth, it’s still a glorified assistant that runs fast but needs supervision. The best teams treat AI like a junior partner — helpful, but not ready to run the show.
Secure.com stands apart by turning AI from a black box into a Digital Security Teammate that works with you. It doesn’t promise full autonomy; it delivers governed intelligence that learns from your context, acts within defined boundaries, and amplifies your decision-making while keeping humans in command.
Here’s how it works in practice. An analyst asks a natural-language question. Secure.com enriches the case, suggests an action, waits for human approval, then logs every step for audit trails. The workflow feels like teamwork, not blind automation.
This approach builds trust where it matters most. You stay in control, with AI handling the labor, not the leverage. It’s fast, transparent, and accountable—AI that acts like a teammate, not a gamble.
Are there any notable failures or breaches in 2025 attributed to overhyped AI cybersecurity tools?
Public stories keep pointing to the same pattern. Overpromised tools that flood the SOC with false positives, hide how they work, or break during tuning. The weak spots are poor data quality, missing guardrails, and no human-in-loop review. If you see high noise, slow MTTR, and surprise gaps during audits, that is your sign that the tool is all pitch and no proof. Ask for proofs of detection, red team replays, and month-over-month drift reports before trust.
What are the best practices for integrating AI into existing cybersecurity frameworks in 2025?Start small in a low-risk slice. Map the workflow in your SIEM and SOAR first. Add an automation framework with clear handoffs to a human-in-the-loop. Track alert quality and MTTR from day one. Keep training data clean. Version prompts and rules. Run red team replays every month. Document failure modes. If the tool cannot show why it made a call, do not let it auto-close tickets.
How are companies measuring the effectiveness of AI in their cybersecurity strategies?They measure signal, speed, and safety. Signal means fewer false positives and more real finds. Speed means lower MTTR and time to first action. Safety means fewer bad auto actions and clear audit logs. Teams also watch analyst load, handoff counts, and rework. A simple scorecard each week gives the truth. If the scorecard stalls, pause rollouts and tune.
How do AI-powered cybersecurity tools handle zero-day threats compared to human analysts?AI helps with speed. It can sift logs, spot odd spikes, and link clues across tools. Humans bring sense-making. They judge impact, shape a plan, and talk to owners. The best setup is both. AI does first pass triage and context. A person checks it fast and moves the fix. That is how you cut noise and keep control.
What role does AI play in incident response and recovery in 2025?AI acts like a steady helper. It enriches events, suggests next steps, and drafts tickets in your SOAR. It grabs intel, maps blast radius, and tracks cleanup. Then humans decide what to block and what to restore. This mix lowers MTTR and keeps weekends sane. The rule stays the same. Clear playbooks. A human-in-loop for risky actions. Reports that show who did what and when.
In 2025 and beyond, AI’s real value is filtering, correlating, and drafting next steps so humans can decide faster. “Autonomous SOC” remains aspirational; governed augmentation is here now. Winners pair AI speed with human judgment—and measure signal, speed, and safety every week.
If you’re evaluating AI security tools, here’s your checklist:

For the latest discoveries in cyber research for the week of November 2-7, 2025.

The cybersecurity industry is short 4.8 million people, yet fully staffed SOCs still drown in 1,000+ daily alerts. The real crisis isn't talent; it's a complete failure of operational leverage.

Many CISOs stumble with automation by chasing tools instead of outcomes, automating low-value tasks, and leaving out human oversight.